For many business leaders, cloud computing is the best way of leveraging computing and storage resources for their operations.
Most have heard about the different types of cloud computing models but are not really clear about the difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. As a result, most decision makers are unable to select the right choice for delivering products and services to their customers.
This decision becomes critical because the market for cloud computing is growing fast. Some experts predict that by 2025, this will be a $832.1 billion industry.
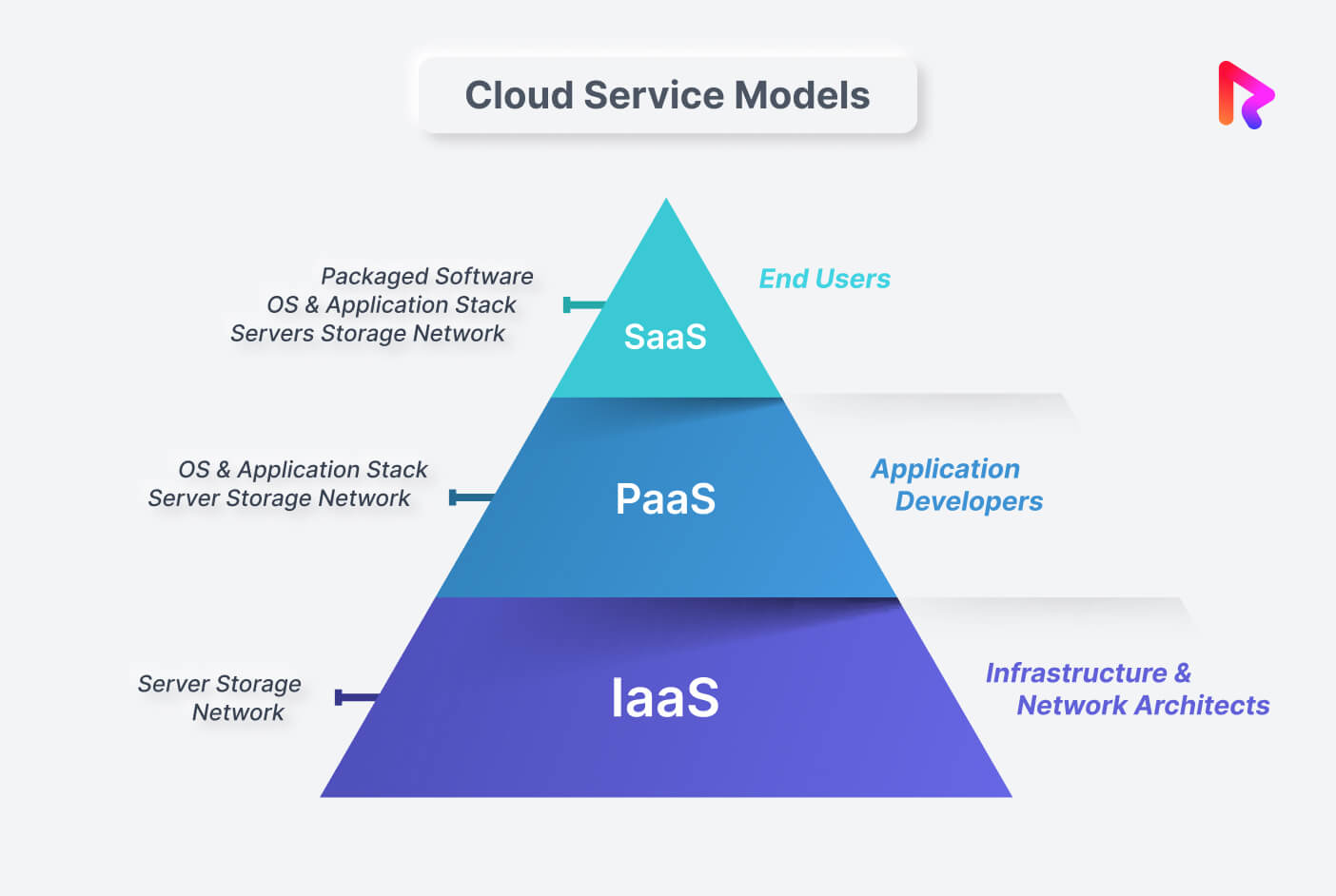
However, the first step in getting the benefit from this multi-billion dollar industry is to select from the three cloud computing models – IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
In this article, we’ll help you pick the right cloud computing model for your business. We’ll explore the distinctive characteristics and benefits of each model.
Let’s start with SaaS, perhaps the most recognizable of the three models.
Table Of Contents
- What is Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)?
- SaaS Examples
- SaaS Benefits
- SaaS Drawbacks
- When to Use SaaS?
- What is Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)?
- PaaS Examples
- Advantages of PaaS
- Disadvantages of PaaS
- When to Use PaaS
- What is Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)?
- Examples of IaaS
- Advantages of IaaS
- Disadvantages of IaaS
- When to use IaaS
- SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: Which is Best ?
- IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)?
SaaS is a software delivery model where applications are hosted on a cloud computing infrastructure.
Users can access it over the Internet through a web browser or application interface instead of installing the software on their computers/desktops or servers.
SaaS providers charge users a subscription fee to access their software. All updates and maintenance-related activities are handled by the SaaS provider.
SaaS Examples
You can find a lot of examples of SaaS, including the following very popular ones:
-
- Salesforce: Sales Cloud Platform.
- Dropbox: used for file storage and sharing platform.
- Google Workspace (formerly GSuite): it’s a productivity tool hosted on the cloud and provides email, document creation, collaboration tools, etc.
- Zoom: one of the most recognizable platforms for video conferencing.
- HubSpot: a cloud-based marketing and sales platform
SaaS Benefits
There are many advantages of using SaaS, including:
-
- Lower costs: SaaS saves money by removing the need for hardware and software purchases and maintenance.
- Scalability: SaaS providers can scale their IT infrastructure to meet the needs of their customers. Businesses can scale the supporting infrastructure as more users access and use the services.
- Accessibility: SaaS applications can be accessed from any device with an internet connection. In fact, a lot of SaaS products offer API that developers can use to integrate these products into customized business solutions.
- Automatic updates: SaaS providers handle updates and maintenance tasks. They ensure that users always have access to the latest version of the software.
SaaS is a very popular cloud computing model because it saves money for end users by removing the need for hardware and software purchases and maintenance.
SaaS Drawbacks
While SaaS offers many benefits, businesses need to consider the following disadvantages:
-
- Dependence on the Vendor: Businesses depend on an infrastructure provider to host their SaaS products and ensure smooth access by the end users. Sometimes, this can be a problem if the provider experiences downtime or goes out of business.
- Limited customization: SaaS applications are typically less customizable than on-premises software, which may limit their usefulness for some businesses.
- Security concerns: Storing data in the cloud can raise security concerns for some businesses, especially those that deal with sensitive data.
When to Use SaaS?
SaaS is an excellent option for firms that merely want access to software applications but wish to refrain from investing in their hardware and software infrastructure. It’s also a perfect option for companies that need to swiftly grow their infrastructure because SaaS providers may easily add and remove users as required. Businesses that need to work across several locations or devices may benefit from SaaS apps, which can be accessed from any location with an internet connection.
What is Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)?
After SaaS, the next most popular cloud computing approach is PaaS, which provides a platform for developers to design, test, and deploy applications.
With PaaS, developers can concentrate on writing code and developing apps rather than worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
On the other hand, the PaaS provider’s job is to handle the servers, storage, and networking, as well as the operating system, middleware, and runtime environment.
PaaS Examples
Microsoft Azure is a great example of PaaS. It provides a stable and scalable platform for web and mobile app development, data storage and analysis, and artificial intelligence. Other PaaS examples include Google App Engine, Salesforce Lightning Platform, and IBM Cloud.
Advantages of PaaS
PaaS is a very popular cloud computing model in developer circles because of the following benefits:
- PaaS offers scalability as a key benefit. According to the demands and the situation, the server resources can be scaled up or down.
- PasS providers offer various components and tools to streamline development workflows. Developers can pick and choose from these tools for faster application development and deployment.
- It can significantly reduce costs because users don’t have to invest in their infrastructure. Most PaaS providers bill on a “pay-as-you-go” model where businesses only pay for the resources they use.
Disadvantages of PaaS
Despite the above advantages, PaaS could offer the following drawbacks:
- PasS providers often don’t offer full control over the infrastructure for the end users.
- PaaS vendors often place restrictions around the support for specific programming languages or frameworks. This is one of the main disadvantages for developers who require specific tools to create their applications.
- Once the application is built on a specific PaaS infrastructure, it is difficult to migrate to a different provider without facing downtime and application instability.
When to Use PaaS
Let’s assume that your business wants to focus mainly on application development and deployment without worrying about investing in an in-house infrastructure management process. In such cases, PasS is a good option for your budget.
Secondly, if you want to quickly scale your operations up and down or have fluctuating traffic demand, you should consider working with a PaaS provider.
However, if your business processes require more control over its infrastructure or you need to use a specific programming language or framework, consider other cloud computing models like IaaS or hybrid cloud solutions.
What is Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)?
The third cloud computing mode is IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service). It provides virtualized computing resources that can be used over the Internet.
IaaS providers offer access to their computing resources so users don’t have to invest and maintain their own physical infrastructure. These computing resources include storage, networking, and computing power as a service. All IaaS providers offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model. It allowed users to pay only for the computing resources they use.
Examples of IaaS
Examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud. These providers offer various services, including virtual machines, storage, networking, and security.
Advantages of IaaS
- IaaS providers allow users to scale their computing resources up or down whenever needed. This will benefit businesses that always experience fluctuating demand for computing resources.
- The end users don’t have to invest in and maintain their physical infrastructure, which can be costly.
- End users can access the IaaS provider’s services from anywhere over an internet connection.
- IaaS providers typically provide robust security measures to protect users’ private data and applications.
- IaaS typically offer a high level of uptime (99.9%) and availability.
Disadvantages of IaaS
The IaaS cloud computing model does have some potential disadvantages, including:
- IaaS services can only be accessed over the Internet, so users are often restricted by the quality and reliability of their Internet connection.
- There is always a chance of data breaches or other security issues despite IaaS providers offering robust security measures.
- End users have less control over the underlying infrastructure with IaaS providers than on-premises infrastructure.
When to use IaaS
Let’s assume that your business needs flexible access to computing resources without investing in and maintaining its physical infrastructure; IaaS is an ideal solution.
Additionally, if you need to quickly spin up new computing resources for temporary projects or experiments, you can use an IaaS cloud computing platform.
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: Which is Best ?
This article has already discussed all cloud computing models, their examples, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases. So the answer to the question “SaaS vs PaaS vs. IaaS: Which is Best?” depends on the specific needs of your business.
- SaaS is best for businesses that need to quickly and easily access software without worrying about installation or maintenance-related tasks.
- PaaS is best for businesses with developers who need to build and deploy web applications quickly and easily.
- IaaS is best for businesses that need complete control over their infrastructure.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS is crucial for making informed decisions in cloud computing. In a nutshell, SaaS offers convenience and accessibility for end users, PaaS provides developers with a platform for creating applications, and IaaS offers flexible infrastructure options.
By choosing the right cloud computing model, businesses can optimize cost-efficiency, scalability, and resource allocation based on their specific needs. When choosing a particular model, businesses should assess factors such as customization and technical expertise requirements to determine which model aligns best with the organization’s goals.
FAQs
Q-1) Is Google a PaaS or IaaS?
Google Cloud is an example of both IaaS and PaaS. Google Compute Engine provides Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) with virtual machines, storage, and networking services. Additionally, Google App Engine offers Platform as a Service (PaaS), which enables developers to build and deploy web applications on the cloud without worrying about infrastructure-related tasks such as installation or maintenance.
Q-2) Which cloud service is PaaS?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that offers users and organizations access to software development tools, application programming interfaces (APIs), and other application deployment services. PaaS allows for the rapid delivery of applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure, such as servers, storage, networking, and operating systems. It lets developers focus on building their applications rather than worrying about infrastructure management. Some of the popular PaaS solutions include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Heroku, IBM Cloud, and Salesforce App Cloud.
Q-3) Is Docker a PaaS service?
Docker is not a PaaS (Platform as a Service) service. Docker is an open platform for developers and sysadmins to build, ship, and run distributed applications on laptops, data center VMs, or the cloud. As such, Docker allows users to develop applications in isolated containers that are easily portable across different environments.
It is important to note that while Docker is a powerful tool, it does not provide the same level of abstraction and automation that a PaaS would. For example, it does not provide auto-scaling or load-balancing capabilities out of the box.