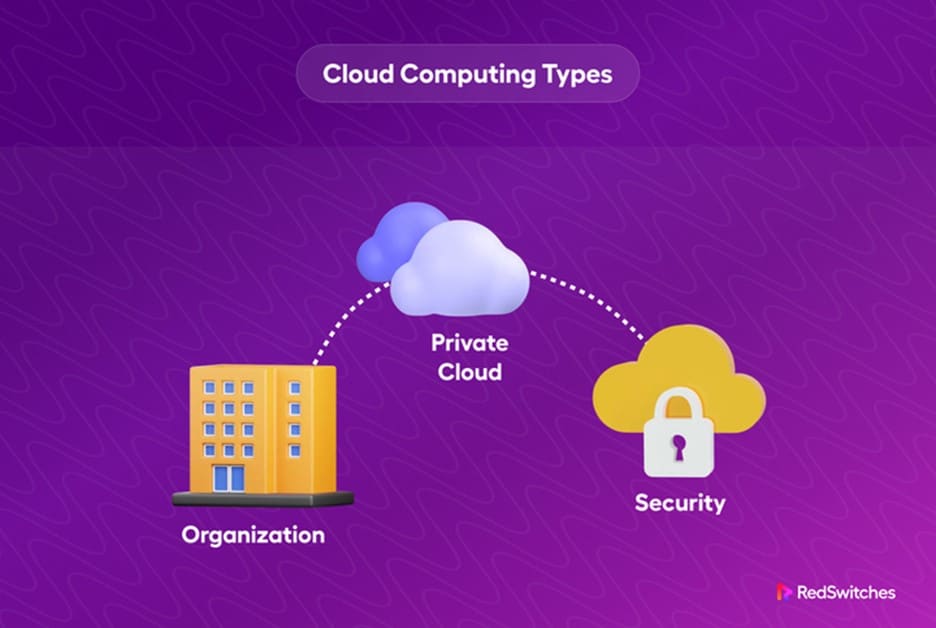
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses and individuals store, access, and process data. With its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and flexibility, cloud computing has become integral to today’s digital landscape. Understanding the 3 types of cloud computing: public, private, and hybrid are crucial for organizations looking to leverage the power of the cloud to meet their unique requirements.
Public cloud computing refers to services and resources provided over the Internet by third-party providers. It offers a shared infrastructure where multiple users can use computing resources on demand. On the other hand, private cloud computing involves dedicated infrastructure exclusively used by a single organization, offering enhanced security and control over data.
Lastly, the hybrid cloud combines the best of both worlds, allowing organizations to leverage public and private clouds to optimize performance, cost-efficiency, and data management. This article explores different cloud deployment models and public vs. private vs. hybrid cloud computing to help you choose one.
Table of Content
- Use Cases of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Deployment Models
- Difference Between Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, And Community Cloud
- Cloud Computing Service Models
- How to Pick the Perfect Cloud?
- Conclusion
- FAQS
Use Cases of Cloud Computing
The most common use cases of cloud computing are email, data storage, and virtual desktops. Cloud computing gives your business more flexibility, allowing you to scale resources and storage to meet business needs.
Common use cases for cloud computing models, public vs. private vs. hybrid, include:
- Software as a Service (SaaS) allows businesses to provide end-user applications to customers via the Internet.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) has resources for developers to design, test, and launch applications.
- Big Data Analytics supports massive databases and makes analytics more accessible.
- Desktop as a Service (DaaS) allows users to monitor performance and increase flexibility through virtual desktop infrastructures.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) gets your company back online as soon as possible after a catastrophic occurrence.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtual machine instances and other services for building a cloud infrastructure.
- Backup as a Service (Baas) allows programmers to delegate responsibility for their apps’ backend operations to a third party.
Cloud Deployment Models
There are 3 types of cloud computing: public, private, hybrid. Let’s discuss what is public, private, and hybrid cloud computing.
Public Cloud
Cloud service providers own and operate public clouds over the internet. The public cloud allows cloud tenants to share infrastructure, storage, and network devices. You use a web browser to access services and manage your account.
Advantages of Public Cloud
- There is no need for capital investments, expensive equipment, or extra space.
- You only pay for what you use, allowing you to scale up or down to get the computing power you need.
- You spend less time managing a data center and can put more effort into more money-making tasks.
- It offers automated, scalable disaster recovery services for improved business performance and compliance
- Public cloud hosting solutions are universal and useful to enterprises in numerous industries.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
- The public cloud’s shared resources nature increases the risk of data loss and breaches.
- You put your data in the cloud service provider’s system and relinquish control over the critical IT infrastructure.
- For a company that needs a customized cloud solution, this architecture won’t work.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is exclusive to one company. Businesses get dedicated servers to fulfill their company’s computing needs via an encrypted private network. The data center resources can be on-site or managed by a third party.
Advantages of Private Cloud
- Private Cloud is an exclusive, dedicated environment just for you and is inaccessible to other groups.
- Private Cloud has exceptional efficiency and dependability, making it a top choice for business needs.
- It’s flexible, and its infrastructure can be changed to meet an organization’s growing needs.
- It’s secure. You can create protocol runs, configurations, and protections based on the company’s workload requirements to keep data safe and secure in the private cloud.
- It is moderately scalable and meets unanticipated demands without compromising security or performance; adding more users or resources doesn’t call for significant changes to the current setup.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
- Due to security precautions, mobile users may have limited access to the private cloud.
- A private cloud solution’s upfront and ongoing costs are far higher than public cloud alternatives.
- On-site infrastructure may have limited scalability options to meet all needs.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud comprises public, private, and on-premises infrastructure, providing a mixed environment for computing, storage, and networking services.
Businesses often choose the hybrid cloud approach for three reasons:
- To get the most out of their on-premises technology investments
- To deal with low latency issues,
- To meet regulatory and data sovereignty requirements.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
- Remote and distant employees can access data on demand with a hybrid cloud.
- Hybrid cloud models optimize IT performance, provide business agility, and speed up market time.
- Business continuity is improved, lowering the likelihood of potential downtime and associated costs.
- It’s ideal for firms that want more data security and control but need a cost-effective way to scale operations.
- It allows organizations more data control and scalability, letting them adjust workloads as business and IT service demands change.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
- Cloud environments are complex, and you might violate compliance rules if you’re not careful.
- Hybrid cloud usage by third-party providers puts your organization in danger of cyberattacks on its central server.
- A hybrid cloud is expensive due to the investment, maintenance, and skill required for on-premises hardware and private cloud components.
Community Cloud
A community cloud is a computing infrastructure that facilitates data sharing across multiple entities. It can be owned and operated by a community organization, a third party, or both.
Advantages of Community Cloud
- Customers can choose their data protection preferences.
- Organizations share cloud computing resources, saving them money.
- The community cloud is flexible, scalable, and works for every user.
- All cloud-based assets, including infrastructure and services, can be pooled and shared among businesses.
- The IT department will have less to do since the data, apps, and systems are in the cloud and thus need less management.
Disadvantages of Community Cloud
- The adoption of data is very slow.
- It is hard for organizations to share responsibilities.
- The cost of a Community Cloud is higher than that of the public cloud.
Difference Between Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, And Community Cloud
Here is the difference between public, private, and hybrid cloud computing:
| Aspects | Public | Private | Hybrid | Community |
| Host | Service Provider | Enterprise | Enterprise | Community (Third Party) |
| Security | Low security | The Most Secure | Moderate Security | High Security |
| Cost | Inexpensive | Expensive | Cost-Efficient | Cost-Efficient |
| Scalability | Very High | Limited | Very High | Limited |
| Examples | Amazon, Google | Microsoft, VMWare | HP, IBM | VMWare, SolaS Community Cloud |
Cloud Computing Service Models
The 3 main cloud computing models are Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service. They help you employ infrastructure, scale your business, and improve manageability.
The three cloud computing models support business activities by reducing capital requirements, providing on-demand access, and lowering IT costs.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Infrastructure as a Service helps you reduce the expense of hardware upgrades to your data center and obtain real-time business insights. You can quickly scale the resources allocated to your IT infrastructure based on your needs.
IaaS aids in the speedy provisioning of new apps and improving the reliability of the underlying infrastructure. It’s typically best for on-premises workloads, such as backup and recovery, dev and test environments, customer-facing websites and web apps, storage systems, analytics, and data warehousing.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS helps developers and businesses build great apps without worrying about infrastructure and operating systems. It reduces the effort required to assess, purchase, set up, and manage all the hardware and software for custom-built apps.
Startups and small enterprises widely use paaS due to its inexpensive, upfront costs, which gives them equal access to cutting-edge tools as their larger counterparts. It also frees businesses to focus on their core competencies without being distracted by routine administrative tasks.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS is beneficial for HR and other enterprise-level support functions. These jobs need employees from different departments to collaborate remotely to share, edit, and publish content.
How to Pick the Perfect Cloud?
When deciding between types of cloud computing, private, public, and hybrid clouds, several considerations, use cases, and constraints should be considered.
This is rarely an either/or scenario in practice, especially considering that most businesses use all three categories of cloud services for their respective strengths.
Even though you probably already use the cloud, it’s crucial to plan how to use each environment to get the most out of it. Prioritize your workloads by identifying their requirements and weighing each approach’s benefits and drawbacks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the various cloud computing models, public, private, and hybrid, is essential for organizations seeking to leverage the benefits of cloud technology. Each type offers distinct advantages and considerations that can significantly impact business operations and outcomes.
Public cloud computing provides cost-effective scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, making it an attractive option for many organizations. Private cloud computing offers enhanced security, control, and customization, making it ideal for industries with stringent data privacy regulations or specific compliance requirements. Hybrid cloud computing combines the best features of public and private clouds, enabling organizations to optimize performance, cost-efficiency, and data management.
Organizations can determine which cloud computing model aligns best with their unique requirements by carefully evaluating their needs, priorities, and objectives. This informed decision-making process ensures that they can maximize the benefits of cloud computing while mitigating potential risks or drawbacks.
Staying knowledgeable about the 3 types of cloud computing, public, private, and hybrid, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and harness the transformative power of the cloud to propel their success in the ever-changing business environment. A company’s best choice is to work with a reliable cloud service provider. Red Hat Switches can help you transition to the cloud and become productive there, so you don’t have to worry about which option best fits your company’s needs.
FAQS
Here are the frequently asked questions concerning types of cloud computing, private, public, and hybrid:
Q-1) Which cloud computing is the best?
The ideal cloud service provider accommodates both your immediate and long-term goals. The public cloud could be the best option for high-volume or variable workloads.
The private cloud could be advantageous for workloads with consistent usage patterns. Hybrid clouds are an all-purpose solution since they can host any workload.
Q-2) Which one to pick?
The choice between public, private, and hybrid cloud systems depends on use cases, factors, and constraints.
It’s good to have an intentional cloud strategy to optimize your use of each cloud environment. Start by outlining the demands of your various workloads, then prioritize them based on each model’s merits and downsides.
Q-3) Which cloud is the safest?
In security issues, public vs. private vs. hybrid cloud computing, private clouds are considered safer because workloads usually run behind the user’s firewall, making them more secure.
Due to multi-tenancy and many access points, public clouds pose more security risks. For hybrids, users can reduce data exposure by migrating workloads and data between environments based on compliance, audit, policy, or security requirements.
Q-4) Which cloud is reasonable?
In a public cloud, you only pay for the resources you utilize. Private cloud owners often buy or rent more hardware and resources to scale up. Normally, private clouds will undoubtedly generate more income and sales.
Hybrid clouds can combine any on-prem, off-prem, or provider cloud to meet your pricing needs.