The IoT world is advancing at an incredible rate. As a result, the demand for quick and sustainable ways to process vast amounts of data has risen.
Fog and cloud are some of the two methods that have become all too common. Do you know how they differ? Read the full fog computing vs. cloud computing comparison below.
Table of Content
- What is Cloud Computing?
- What is Fog Computing?
- What is the Difference Between Fog Computing and Cloud Computing?
- The Pros & Cons of Cloud Computing For IOT
- The Pros and Cons of Fog Computing
- Fog Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Key Differences
- Key Takeaways
What is Cloud Computing?
Most people do not understand the difference between fog computing vs. cloud computing. Cloud computing is the on-demand provision of computer processing power, data storage, and applications available over the internet.
Most cloud service providers (CSPs) offer this technology as a pay-as-you-go service. It includes SaaS (Software as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), or IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service).
With cloud computing, users do not have to own any technologies they use for their work, whether software or hardware. Anyone can rent cloud computing power from the CSPs.
Also Read: 6 Key Differences: Cloud vs On Premise Computing Revealed!
What is Fog Computing?
Link to image: https://pixabay.com/images/search/internet%20of%20things%20and%20cloud/?manual_search=1
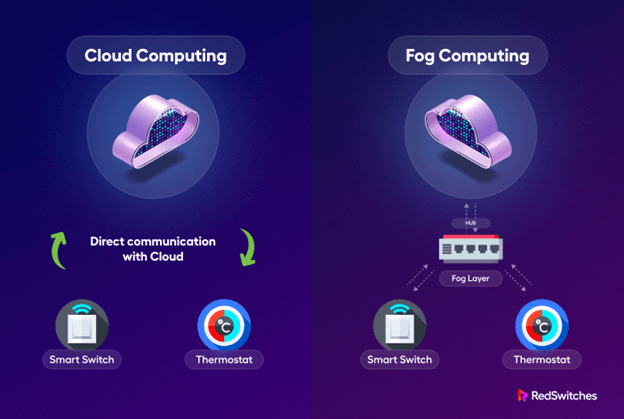
Fog computing is a more decentralized form of cloud computing whereby the computing technology is between a cloud and a data source or another data center. It is an extension of cloud computing.
It comprises several edge nodes that assist you with a direct connection with any physical hardware. As such, it has the potential to enable instant connections.
The fog layer devices typically perform operations linked to networking. They include gateways, hubs, routers, and bridges. These devices have the potential to perform both networking and computational operations simultaneously.
While fog devices are resource-constrained compared to cloud servers, their decentralized nature and geological spread enhance service reliability, covering vast areas. In essence, fog computing is a physical location of computing devices much closer than cloud servers.
What is the Difference Between Fog Computing and Cloud Computing?
Below is a fog vs. cloud computing table outlining the distinct differences between the two systems:
| Key Differences | Fog Computing | Cloud Computing |
| Location Awareness | Location awareness is partially supported in fog computing. | Location awareness is fully supported in cloud computing. |
| Mobility | Fog computing supports mobility. | Mobility is limited in cloud computing. |
| Number of Server Nodes | There is an enormous number of server nodes in fog computing. | Only a few server nodes are available in cloud computing. |
| Data Integration | It’s possible to integrate multiple data sources and devices in fog computing. | Cloud computing allows for the integration of multiple data sources |
| Location of Service | Services are offered at the edge of the local network in fog computing. | Services are provided within the network in cloud computing. |
| Speed | Fog computing supports excellent speeds, even higher than those of cloud computing. | Depending on the VM connectivity, cloud computing has high speeds |
| Security | Fog computing’s security level is high | When compared to fog computing, cloud computing has a low level of security |
| Delay | Fog computing experiences low latency | Cloud computing has a higher latency level as compared to fog computing |
| Responsiveness | Fog computing’s time of responsiveness is high | The response time of cloud computing is low |
| Capacity | Fog computing lowers the quantity of data conveyed to cloud computing | In cloud computing, there is no reduction in the data amount either sent or converted |
| Communication Mode | Fog computing supports wireless communication: WiFi, WLAN, 3G, 4G, ZigBee, etc., or wired communication (part of the IP networks) | Cloud computing only works with the user’s IP Network |
| Geographical Distribution | Fog computing is decentralized and distributed | The cloud computing location is highly centralized |
| Dependence on the Quality of Core Network | Fog computing can work either in a weak or strong network core | Cloud computing needs a robust network core |
| Working Environment | Fog computing’s working environment is indoors (cafes, houses, etc.) or outdoors (bus stations, streets, etc.) | Cloud computing needs unique data center buildings that are fitted with air conditioning systems. |
The Pros & Cons of Cloud Computing For IOT
Here are the pros and cons of cloud computing for IoT:
| Pros | Cons |
| Cloud computing reduces the infrastructure costs associated with in-house server farms. This includes the cost of hardware acquisition, maintenance, software installations, the staff needed to operate the machines, energy costs, etc. | Businesses can only access their data on the cloud using the internet. This is a disadvantage when there is low or zero connectivity. |
| Cloud storage makes data consolidation easier since it is distributed amongst bi-costal data centers, and there is rarely any need to sync it now and then. | Moving to the cloud attracts an ongoing cost, while an on-premise data farm only requires one substantial initial investment. |
| Cloud storage is a much more secure option than an on-premise data center. It relies on enterprise-level security that is highly sophisticated compared to what most small businesses can afford in-house. | The cloud requires superb internet speed with high bandwidth, and service outages, which can cause business downtime, are always possible. |
| Moving to the cloud maximizes uptime and minimizes the losses associated with unplanned downtimes. | Businesses have limited or sometimes zero control over the cloud infrastructure since they do not own it. |
| Cloud computing allows employees to collaborate digitally. They can share and edit documents and files in real-time while working from anywhere worldwide, enhancing company efficiency and productivity. | Even if CSPs implement the best security standards, data security is still a huge concern since the public cloud is run over the internet. |
| Cloud storage services can increase an organization’s storage capacity in minutes.
In contrast, doing the same with a local server could have taken weeks or months. Cloud thus ensures quick scaling for organizations that are rapidly growing. |
Vendor lock-in occurs when there are complications when transferring services between vendors who offer different platforms. |
| Cloud computing automates routine backups, making it unnecessary for in-house staff to waste time on daily backup schedules. | |
| Cloud computing frees up office space and eliminates the need to plan for future office expansion, allowing organizations to utilize every square inch of space. | |
| A cloud services provider handles the essential data compliance regulations, meaning that businesses never have to worry about incurring violations. | |
| Cloud computing allows a company to save energy, lowering its carbon footprint and making the planet more sustainable. |
The Pros and Cons of Fog Computing
The pros and cons of fog computing are outlined in the table below:
| Pros | Cons |
| Fog computing offers more privacy because businesses can analyze sensitive data locally before conveying it to a centralized cloud infrastructure. | Fog computing can be challenging to understand, mainly due to its complexity. It relies on numerous devices located at varying locations, each storing and analyzing its own data set. |
| Developing fog applications and deploying them anytime is easy, increasing productivity. | Fog nodes consume too much power as compared to a centralized cloud infrastructure. |
| Fog computing offers more security because devices connect at different endpoints rather than at a centralized location. It is, therefore, easier to identify and neutralize threats before they affect the entire network. | Trust and authentication in fog networks are almost impossible due to the vast nature of the systems’ computing scale. |
| Fog computing has a lower bandwidth requirement since it can process the data locally. | Cloud storage and controller devices are distributed over vast areas, making maintenance a headache. |
| Since fog computing allows for data processing at the data source nearest to a business, the responses are instant, which is excellent for time-sensitive services. | Complex scheduling as tasks move between fog nodes, client devices, and back-end cloud servers. |
| Fog nodes like factory floors, cars, and tracks can survive harsh environmental conditions. | Achieving data consistency in fog networks is challenging and requires plenty of effort. |
| Due to their natural mobility, fog nodes can join or leave the network anytime. |
Fog Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Key Differences
Link to picture: https://unsplash.com/s/photos/cloud-computing
When it comes to cloud vs. fog computing concepts, the two have plenty of similarities. But still, they differ on some key aspects, as outlined below:
Architecture
In cloud networks, information must travel to the server from one user’s device and back down to the other users. However, in fog networks, the information gets processed at a local level.
Fog has a decentralized architecture with millions of small nodes that together comprise the entire network being as close as possible to the client hardware.
Storage Capacity and Computing Capabilities
The cloud has a higher potential than the mist.
Remote data centers are the hubs of data processing in cloud computing. For fog, processing and storage occur at the network’s edge, nearer to the information source, enhancing real-time control.
Response Mechanism
The cloud targets a deep, long-term analysis due to a sluggish response.
Fog aims for a shorter-term edge analysis due to the swift response.
Latency
The centralized nature of a cloud system leads to high latency, while fog systems experience low latency due to their decentralized nature.
In cloud networks, information travels to the server from one user’s device and back down to the others. In fog networks, the information gets processed at a local level.
Internet Requirements
Cloud computing systems require robust and reliable internet connections.
Fog networks rely on a decentralized approach, with systems at the network’s edge, such as sensors or devices, storing and processing data.
Security
The distributed architecture of a fog system makes it more secure than a cloud computing system.
Key Takeaways
- Fog computing vs. cloud computing is a hot debate due to the massive demand for quick and sustainable data processing mechanisms.
- Cloud computing delivers on-demand services such as CPUs, applications, and data storage over the internet to paid users.
- Fog computing is a highly decentralized computing system. It is an intermediary between a data source and a cloud or another data center.
- One key difference between fog computing and cloud computing system is that fog is decentralized and has many server nodes. In contrast, a cloud is centralized and has a few server nodes.
- The pros of cloud computing are that it lowers IT infrastructure costs and allows employees to collaborate effectively, even remotely. Its cons include that it can only be accessed via the Internet. Businesses always need a fast and reliable connection to avoid downtime.
- The pros of fog computing include that it offers more privacy and has a lower bandwidth requirement since data is processed locally. Its cons include being too complex, making it difficult to understand or develop trust and authentication.
- Both fog and cloud computing systems have plenty of similarities. Still, they differ in numerous aspects, including the number of nodes each system relies on and the anatomy of their computing infrastructure.
As the demand for information increases, more networking channels will emerge. The fog computing vs. cloud computing battle will continue as businesses seek to manage and disseminate data more quickly and sustainably.
If you’re looking for the best dedicated server provider to increase efficiency, contact RedSwitches today. We offer a wide range of services at unbeatable prices that can be customized in every way to fit your needs.
Contact us now or check out our resources to continue exploring cloud computing and much more.